Read a File While It Is Being Writing Python
Files are used to shop and organize data on a disk. We often use files when we need to shop information permanently on a difficult disk. For example, say we are edifice a software organization that maintains student records. Now, we need to store the student data permanently for futurity employ. For this purpose, nosotros tin can use files to store data, and later on, nosotros can open up these files and access the stored data at any time.
Reading and writing files are very common functions in Python. It is piece of cake to create, read, and edit files in Python. Python comes with congenital-in functions for reading and writing files. Yous can open, write, and read files using the Python congenital-in functions. The file operations are performed in the following sequence:
- Open up a file
- Read/write file
- Close file
Using Python, you can create text files and binary files. Text files store data in the grade of characters and each line ends in a newline graphic symbol ('\n'). In binary files, information is stored in the class of bytes (1 and 0).
In this commodity, y'all will larn:
- Some of the dissimilar file modes in Python
- How to open a file
- How to create a file
- How to write information to a file
- How to read a file
Different File Modes in Python
Modes in Python describe the type of operation to be performed on the file. When opening a file, you must specify the fashion. Every file has a file handle. The file handle acts like a cursor that specifies where to write and read data. It is a type of location pointer. The following include some of the unlike access file modes in Python:
| Manner | Description |
| r | Opens the file in reading manner. This mode is selected by default if you do not define whatever mode while opening the file in Python. |
| w | Writes a file. This way creates a file if the file does not exist already and overwrites the data in the file. |
| r+ | Used to read and write the file. It shows an fault if the file does not exist. |
| a | Opens the file in append fashion. The file handle is located at the cease of the file. This mode does not overwrite the existing data but starts writing data at the finish of the file. A new file is created if the file does not exist. |
| a+ | Opens the file for reading and writing. This opens the file in append mode for writing. The information is inserted at the end of the file. A new file is created if the file does not be. |
| t | Opens the file in text mode. |
How to Open up a File
To open a file in Python, use the built-in open() function. The open() function takes two arguments as an input, i.e., the name of the file and the fashion of operation. This part returns the file object as an output. There is no demand to import whatsoever module to employ the open() function. The post-obit is the syntax of the open() function:
file_object = open ("file_name", "way")
Hither, 'file_name' represents the name of the actual text file, while 'mode' represents the file access or file functioning fashion. Yous can also place r earlier 'file_name,' if the file name includes special characters. The r is placed as follows:
=file_object = open (r"file_name", "style")
For example, the file proper name could be: "F:\newfolder\myfile.txt"
How to Create a File
The open() function can be used to create files in Python. Use the suspend way (a) inside the open() function to create the file. Create a file using the lawmaking given below:
file = open ( "sample.txt" , "a" )
Hither, a new file object is created. The file object is named "file." The name of the newly created text file is "sample.txt." The text file is opened in append mode. It will create the new file if the file does non be already. After creating the file, you must close the file in the following way:
The born close() function is used to close the file.
How to Write Information to a File
There are two functions in Python used for writing data in a file:
- write()
- writelines()
The write() part is used to write single line or single string data to a file, while the writelines() function is used to write multiple lines of data to a text file. Let us see some examples of writing data to a file.
Using the write() Office
In this instance, nosotros are using the write() function to write information to a file. The file is opened in writing fashion. "\n" is placed to specify the end of the line.
# creating a new file object and opening a file in writing manner
file = open ( "sample.txt" , "west" )
# writing single line to a file
file.write ( "Welcome to the linuxhint \northward" )
# writing another single line to a file
file.write ( "Welcome back" )
#closing the file
file.shut ( )
Output
The lines have been written in the text files.
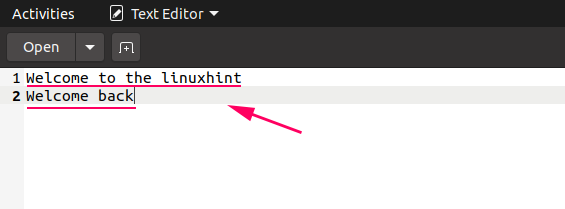
If we open the file in writing mode and ask the write() office to write more than lines to the file, it volition overwrite the previous data and new data will be added into the text file.
# creating a new file object and opening a file in writing way
file = open ( "sample.txt" , "w" )
# writing single line to a file
file.write ( "Hello Everyone \due north" )
# writing some other single line to a file
file.write ( "This is the replaced string" )
#closing the file
file.close ( )
Output
In the output, information technology can be seen that the previous information is replaced and new data is added in its place in the text file.
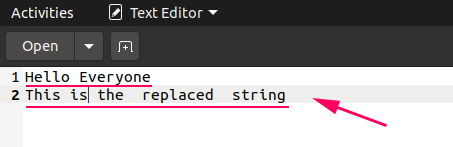
If we want to keep both the previous and the new data in the file, and so nosotros tin open the file in suspend manner, like this:
# creating a new file object and opening a file in append mode
file = open ( "sample.txt" , "a" )
# writing unmarried line to a file
file.write ( "Hullo Anybody \n" )
# writing some other single line to a file
file.write ( "This is the replaced string\n" )
# writing another new single line to a file
file.write ( "This is the newly added cord string\northward" )
#closing the file
file.close ( )
Output
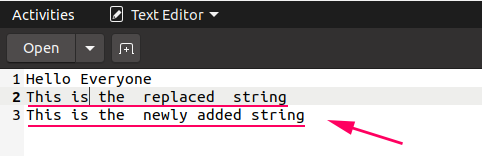
Using the writelines() Part
The writelines() function is used to write multiple lines in a text at one time, as follows:
# creating a new file object and opening a file in writing way
file = open up ( "file1.txt" , "w" )
# storing multiple string data in a variable
str = [ "How-do-you-do anybody\northward" , "Welcome to the linuxhint\northward" , "we are using writelines function\n" ]
# using writelines functions to write information in a file
file.writelines ( str )
#closing the file
file.close ( )
Output
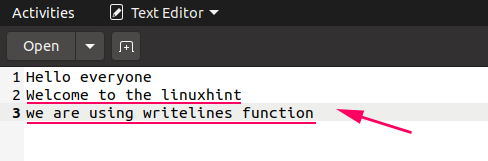
How to Read a File
To read a file in Python, commencement, open the file in reading mode. In that location are three congenital-in functions in Python for reading a file. These include the post-obit:
- read()
- readline()
- readlines()
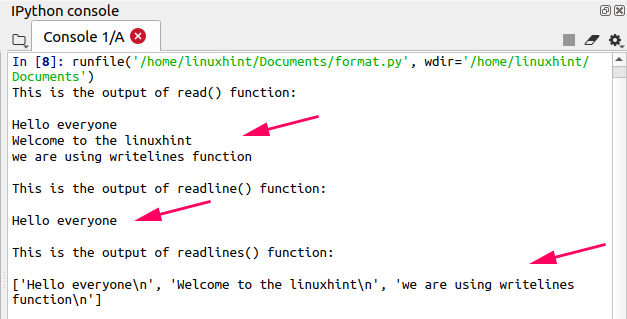
read(): Used to read the information from a file; returns the whole data in the grade of cord.
readline(): Reads a line of data from a file; only returns the commencement line.
readlines(): Reads all existing lines from a file; returns it in the form of a list.
The seek() role is used to change the file handle position. When reading information in the file, the file handle positions itself at the stop of the file. Thus, a file handle is similar a cursor, with the seek() function every bit the means to move the cursor.
Let us see an example of reading data from the file.
# opening a file in read mode
file = open ( "file1.txt" , "r" )
# using read() function to read the data from the file
# storing the lines in a variable
data= file.read ( )
# press the information
impress ( "This is the output of read() function: \n" )
print (data)
# using seek() function to bring the file position in start
file.seek ( 0 )
# using readline() office to read the data from the file
# storing the lines in a variable
information= file.readline ( )
# press the data
print ( "This is the output of readline() office: \n" )
print (data)
# using seek() function to bring the file position in commencement
file.seek ( 0 )
# using readlines() function to read the data from the file
# storing the lines in a variable
data= file.readlines ( )
# printing the data
print ( "This is the output of readlines() function: \n" )
print (data)
#closing the file
file.close ( )
Output
Conclusion
It is often necessary to store data or data to a file. In Python, y'all tin easily create, write, and read files using the Python built-in functions. In that location is no need to import other modules into your program when y'all want to read, write, and create files. You can also use multiple congenital-in access modes while using the files. In this article, nosotros have explained how to read and write files in Python with some uncomplicated examples.
Source: https://linuxhint.com/reading_writing_files_python/
0 Response to "Read a File While It Is Being Writing Python"
Post a Comment